
Amputation and 4 Amputation Nursing Care Plans and Nursing Diagnosis My Nursing Papers
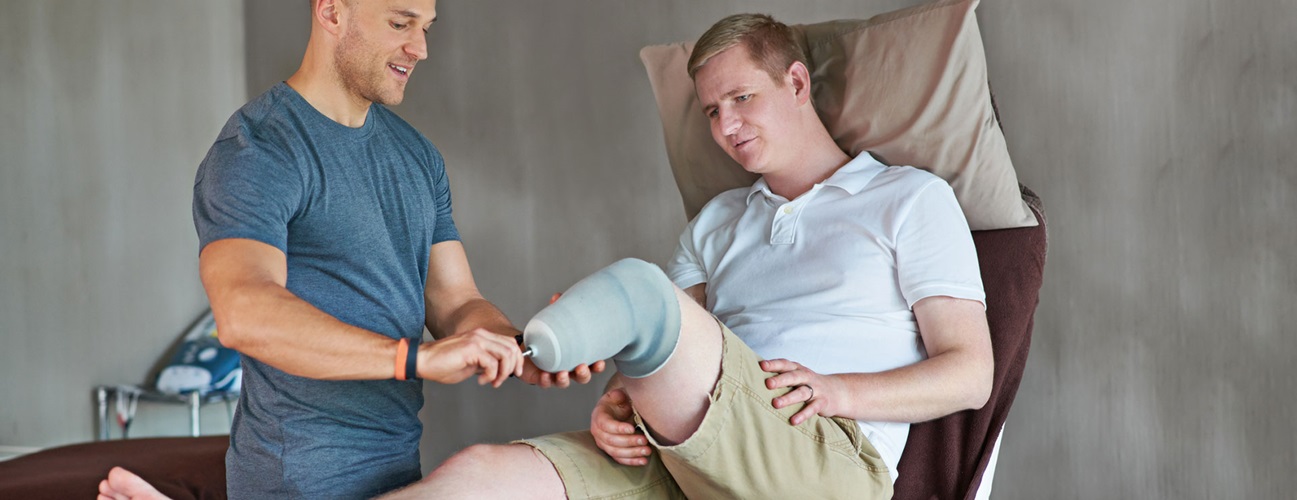
Amputation is the surgical removal of all or part of a limb due to a chronic condition or catastrophic injury. Medical advances in preventive approaches have resulted in a drop in the overall rate of amputations in the United States. Amputations due to chronic diseases like diabetes, on the other hand, have stayed constant or even increased.
Nursing 300/301 Nursing Care Plan Assessments, Interventions
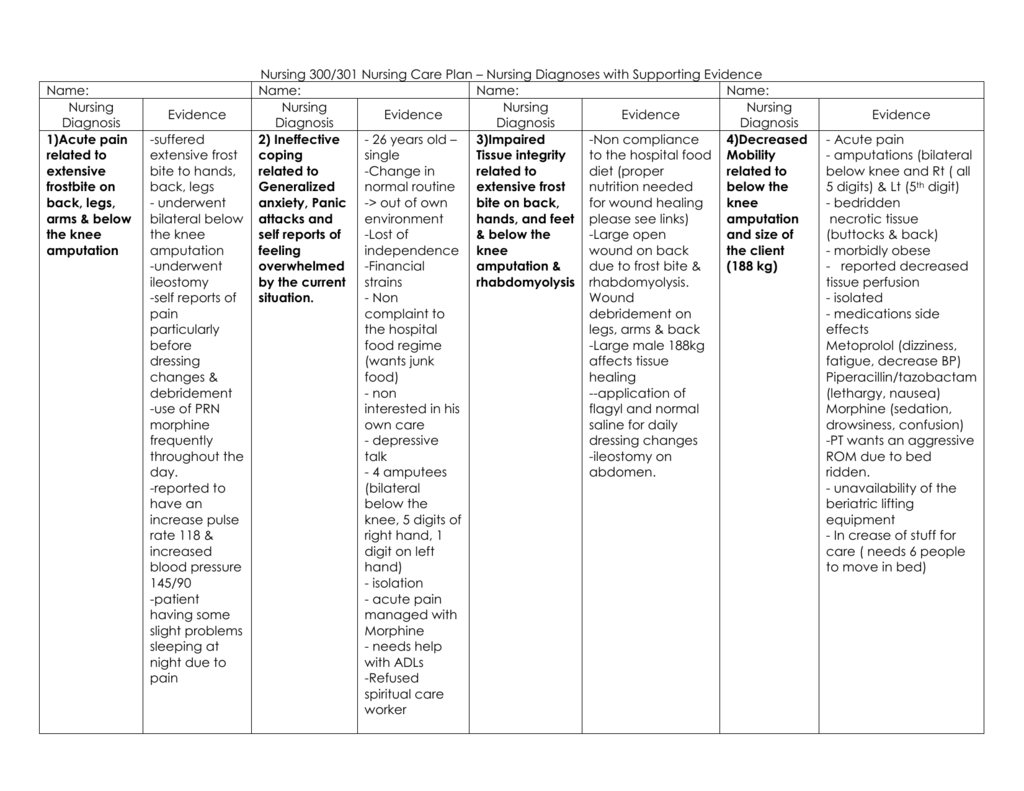
Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired Physical Mobility Causes of Related Factors: Loss of a limb (especially a lower extremity); pain/discomfort; impairment of perception (altered sense of balance). Possibly evidenced by the: Reluctance to initiate motion Coordination deficits; less muscle strength, control, and mass Defining Characteristics

amputations nursing care Nursing care, Wound care nursing, Medical surgical nursing
Richard L. Pullen, Jr., is professor of nursing and assistant director of the ADN program at Amarillo College in Amarillo, Tex, and a member of the Nursing2010 editorial board. A patient is scheduled for a below-the-knee amputation. What postoperative nursing care priorities should I prepare for?—C.H., W.VA.

Houston Amputation Injury Lawyers Armstrong Lee & Baker LLP
Following a thorough assessment, a nursing diagnosis is formulated to specifically address the challenges associated with amputation based on the nurse 's clinical judgement and understanding of the patient's unique health condition.

Amputation Nursing Osmosis Video Library
1. Assessing Mobility Status and the Need for Assistance 2. Safe Client Handling 3. Providing a safe environment for the client 4. Proper Use of Assistive Devices 5. Range of Motion Exercises and Physical Therapy 6. Client Positioning, Moving, and Transferring 7. Client and Caregiver Education to Prevent Falls and Injuries

nursing amputation Google Search Rehab Nursing, Nursing Study Tips, Nursing Cheat, Nursing
Overview Concept maps Many types, variations, layouts Primary diagnosis Typically in center of map Connects to Contributing factors Medications Labwork Patient education Nursing diagnoses Interventions Evaluations Nursing Points General Nursing diagnosis Impaired physical mobility Encourage patient to perform prescribed exercises

In general, amputation of limbs is the result of trauma, peripheral vascular disease, tumors
Amputation is when an extremity is separated from the rest of the body.This most often involves a limb or a part of it like a digit, but can also involve a portion of the nose or ears.. Now, the causes of amputation may include trauma, such as a motor vehicle crash or power tool injuries. Amputation can also be performed surgically to prevent or manage a condition, such as tissue death and.

First Aid for Traumatic Amputation
2 Case Type / Diagnosis: Practice Pattern: 4J: Impaired Gait, Locomotion, and Balance and Impaired Motor Function Secondary to Lower Extremity Amputation. Other Practice Patterns may be applicable as well. ICD 9 Codes: 84.1, 84.3, 84.13, 84.14, 84.15, 84.16, 84.17

4 Amputation Nursing Care Plans Nurseslabs Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD/PAD) Nursing
Below-the-knee: removal of the leg 5″ to 7″ (12.5 to 18 cm) below the knee. Knee disarticulation: removal of the patella, with the quadriceps brought over the end of the femur, or fixation of the patella to a cut surface between the condyles (known as the Gritti-Stokes amputation) Above-the-knee: removal of the leg from 3″ (7.6 cm) above.

4 Amputation Nursing Care Plans • Nurseslabs Nursing Care Plan, Nursing Diagnosis, Vascular
NURSING DIAGNOSIS: Infection, risk for Risk factors may include Inadequate primary defenses (broken skin, traumatized tissue) Invasive procedures; environmental exposure Chronic disease, altered nutritional status [Not applicable; presence of signs and symptoms establishes an
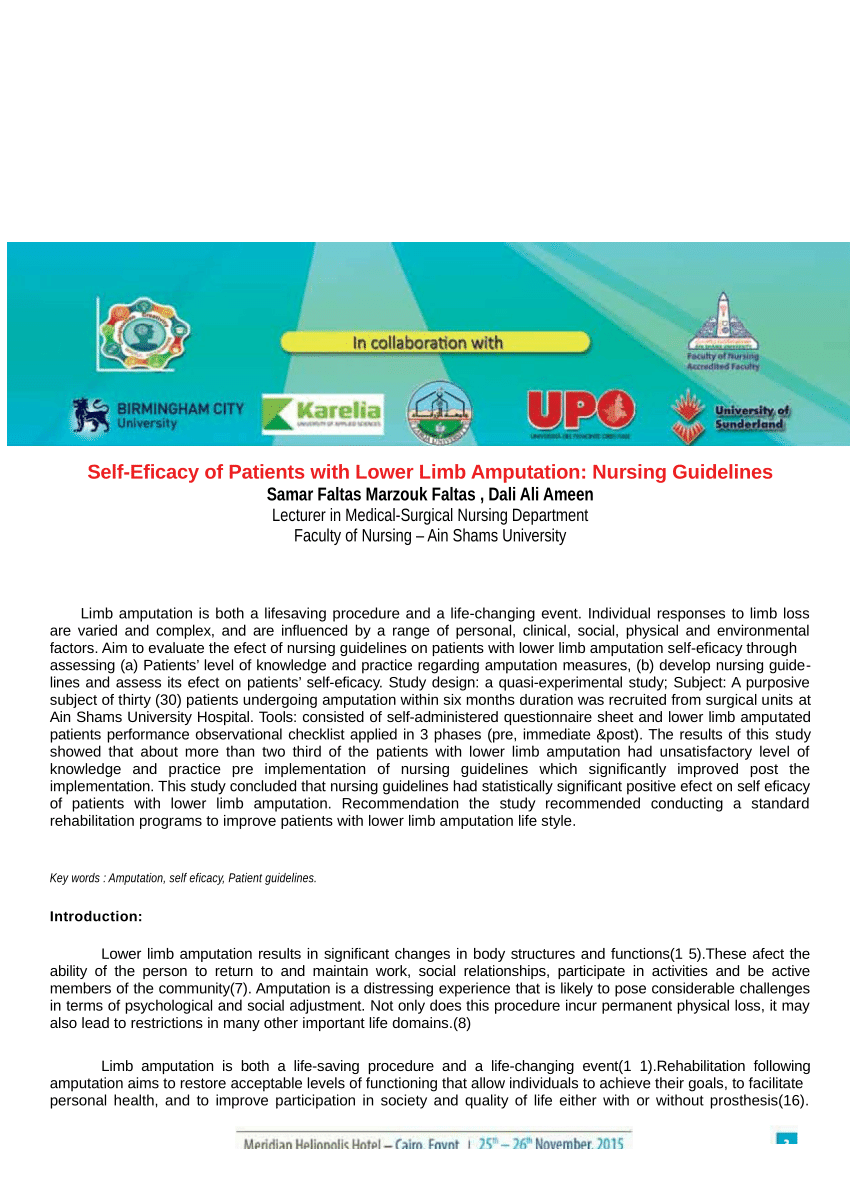
(PDF) SelfEficacy of Patients with Lower Limb Amputation Nursing Guidelines
A multidisciplinary approach which includes surgical technique, regional analgesia, pharmacological agents, physical therapy and psychotherapy are all key components in the peri-operative care of an amputee that can have a strong impact in decreasing the risk of PLP.

Amputation Or Not? Making The Choice For Amputation Prosthesis Prosthesis Advice!
Evaluation Conclusion FAQs Related posts: Introduction A nursing care plan for amputations focuses on helping the patient through the life-altering event of having a limb removed. This plan includes holistic assessment and evaluation, nursing diagnosis and interventions, outcome statements and rationales, and patient evaluation and education.

In general, amputation of limbs is the result of trauma, peripheral vascular disease, tumors
A nursing diagnosis is a clinical judgment concerning a human response to health conditions/life processes, or a vulnerability to that response, by an individual, family, group, or community.

4 Amputation Nursing Care Plans Nurseslabs
Situational Low Self Esteem Nursing Care Plan 1. Amputation. Nursing Diagnosis: Situational Low Self-Esteem related to the loss of a part of the body or a shift in functional capacity secondary to amputation as evidenced by anticipated lifestyle adjustments, fear of criticism, unpleasant sentiments about the body, an emphasis on past strength.
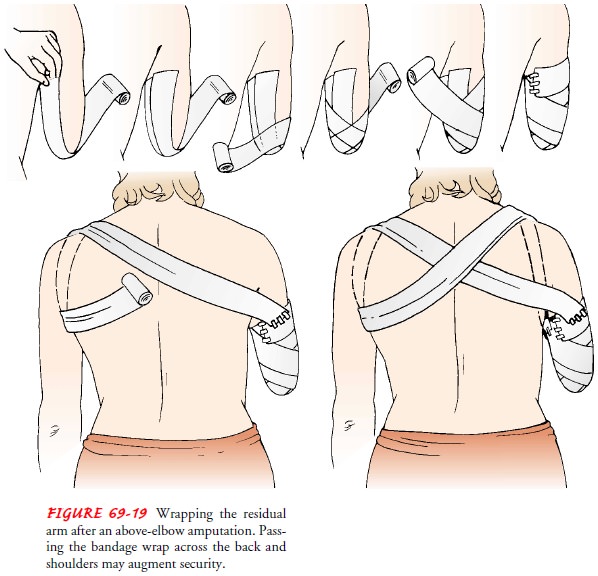
Nursing Process The Patient Undergoing an Amputation
Overview Amputation Loss of limb Patient centered care Nursing Points General Reasons for amputation Disease Diabetes->poor circulation, wounds PVD or arterial disorders->lack of blood/oxygen to tissues, wounds Injury Tumor Severe infection->osteomyelitis Amputation locations Leg Above knee Below knee Foot
About Leg Amputation.
Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired Physical Mobility related to the clinical manifestations of psoriatic arthritis, as evidenced by distal interphalangeal predominant (DIPs) in the fingers, morning stiffness of wrists and elbows, pain score of 8 to 10 out of 10, fatigue, disinterest in ADLs due to pain, verbalization of tiredness and generalized weakness